Page 9 - 9788179931806
P. 9
STORM STORY 8-9
Westerlies and easterlies
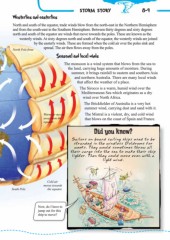
North and south of the equator, trade winds blow from the north-east in the Northern Hemisphere
and from the south-east in the Southern Hemisphere. Between thirty degrees and sixty degrees
north and south of the equator are winds that move towards the poles. These are known as the
westerly winds. At sixty degrees north and south of the equator, the westerly winds are joined
by the easterly winds. These are formed when the cold air over the poles sink and
North Pole front spread. The air then flows away from the poles.
Seasonal and local winds
The monsoon is a wind system that blows from the sea to
the land, carrying huge amounts of moisture. During
summer, it brings rainfall to eastern and southern Asia
and northern Australia. There are many local winds
that affect the weather of a place.
The Sirocco is a warm, humid wind over the
Mediterranean Sea which originates as a dry
wind over North Africa.
The Brickfielder of Australia is a very hot
summer wind, carrying dust and sand with it.
Warm air moves The Mistral is a violent, dry, and cold wind
away from the that blows on the coast of Spain and France.
equator.
Did you know?
Sailors on board sailing ships used to be
stranded in the windless Doldrums for
weeks. They would sometimes throw all
their cargo into the sea to make their ship
lighter. Then they could move even with a
light wind.
South Pole Cold air
moves towards
the equator.
Now, do I have to
jump out for this
ship to move?
Westerlies and easterlies
North and south of the equator, trade winds blow from the north-east in the Northern Hemisphere
and from the south-east in the Southern Hemisphere. Between thirty degrees and sixty degrees
north and south of the equator are winds that move towards the poles. These are known as the
westerly winds. At sixty degrees north and south of the equator, the westerly winds are joined
by the easterly winds. These are formed when the cold air over the poles sink and
North Pole front spread. The air then flows away from the poles.
Seasonal and local winds
The monsoon is a wind system that blows from the sea to
the land, carrying huge amounts of moisture. During
summer, it brings rainfall to eastern and southern Asia
and northern Australia. There are many local winds
that affect the weather of a place.
The Sirocco is a warm, humid wind over the
Mediterranean Sea which originates as a dry
wind over North Africa.
The Brickfielder of Australia is a very hot
summer wind, carrying dust and sand with it.
Warm air moves The Mistral is a violent, dry, and cold wind
away from the that blows on the coast of Spain and France.
equator.
Did you know?
Sailors on board sailing ships used to be
stranded in the windless Doldrums for
weeks. They would sometimes throw all
their cargo into the sea to make their ship
lighter. Then they could move even with a
light wind.
South Pole Cold air
moves towards
the equator.
Now, do I have to
jump out for this
ship to move?