Page 8 - 9788179931806
P. 8
Surface winds
The earth has three types of winds blowing
close to its surface—those that blow over North Pole
a large area throughout the year;
those that blow only during a
Satellites are used to study moisture particular season;
formation and the movement of wind.
and those that blow Easterlies
over small areas. 60° N
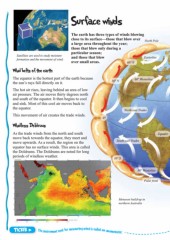
Wind belts of the earth
The equator is the hottest part of the earth because 30° N 60° Westerlies
the sun’s rays fall directly on it.
The hot air rises, leaving behind an area of low North east Trades
air pressure. The air moves thirty degrees north
and south of the equator. It then begins to cool 0°
and sink. Most of this cool air moves back to
the equator.
This movement of air creates the trade winds.
Windless Doldrums
As the trade winds from the north and south Equator
move back towards the equator, they meet and
move upwards. As a result, the region on the South east Trades
equator has no surface winds. This area is called 30° S
the Doldrums. The Doldrums are noted for long
periods of windless weather.
60° Westerlies
Polar front
Monsoon build-up in
northern Australia
TICKER The instrument used for measuring wind is called an anemometer.
The earth has three types of winds blowing
close to its surface—those that blow over North Pole
a large area throughout the year;
those that blow only during a
Satellites are used to study moisture particular season;
formation and the movement of wind.
and those that blow Easterlies
over small areas. 60° N
Wind belts of the earth
The equator is the hottest part of the earth because 30° N 60° Westerlies
the sun’s rays fall directly on it.
The hot air rises, leaving behind an area of low North east Trades
air pressure. The air moves thirty degrees north
and south of the equator. It then begins to cool 0°
and sink. Most of this cool air moves back to
the equator.
This movement of air creates the trade winds.
Windless Doldrums
As the trade winds from the north and south Equator
move back towards the equator, they meet and
move upwards. As a result, the region on the South east Trades
equator has no surface winds. This area is called 30° S
the Doldrums. The Doldrums are noted for long
periods of windless weather.
60° Westerlies
Polar front
Monsoon build-up in
northern Australia
TICKER The instrument used for measuring wind is called an anemometer.