Page 12 - Turning Trash to Treasure: Development of Waste-to-Energy Technologies
P. 12
in operation for processing MSW—of Two plants were built in Italy in 1978, been added. Modern waste-to-energy
these, two are in Delhi and one is in one in Germany in 1981, Laval (France), technologies have been commercially
Jabalpur at various levels of maturity. Chatel St. Denis (Switzerland), five plants deployed, especially in Europe, Japan,
Anaerobic digestion-based MSW to in Sweden, and one 800 TPD capacity Australia, China, and the USA. In the
energy projects got commissioned by plant at Edin Prairie, Minnesota, USA. The USA, there are 86 WtE plants—about
utilizing the incentive schemes of the RDF was used for generating power or 12% of waste is combusted for energy
Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy used in cement plants. recovery—mostly ‘mass burn’. The
Sources (now Ministry of New and The Department of Science and number of plants built during 2008–11
Renewable Energy), Government of Technology, Government of India, had all over the worldis shown in Figure 2.
India. A number of efforts were made installed a refuse derived fuel (RDF) No new plants have been built in the US
to install facilities for AD of municipal plant at Deonar in Mumbai in 1994; since 1995.
garbage. Two attempts were made on a the plant had a capacity to process 80 In India, as of now, two waste-to-
large scale—first at Nagpur followed by TPD garbage. Almost at the same time, energy plants are functional in Delhi,
the second in Lucknow for generating a 5 TPD capacity plant was installed in one based on mass burn option
electrical power from municipal Bengaluru by a private company. The operating at rated capacity, another
garbage. The project at Nagpur plant in Mumbai had initial difficulty in one based on RDF processing is yet to
was abandoned at an early stage of acquiring good calorific value. Both the operate commercially, There is another
construction by the entrepreneur. The plants were subsequently closed but the plant commissioned at Jabalpur which
project at Lucknow was commissioned DST technology was further developed is yet to attain commercial level. More
successfully but its actual operation and marketed by the Technology RDF plants are on the anvil, boosted by
got embroiled in controversy about the Information Forecasting and Assessment the demand from cement plants aiming
quality of garbage being supplied by Council (TIFAC). Two plants were set at fuel substitution to achieve desired
the municipal corporation, almost from up—one in Hyderabad (200 TPD in thermal substitution rates.
the beginning. Also, the project cost was 1999, later expanded to 700 TPD with It is also estimated by Ministry of New
about `16 crore per MW and there was generation of 6.6 MW power in 2003) Renewable Energy, Government of India,
no cushion for lesser than calculated and one in Vijayawada (600 TPD with a in its deposition to Task Force at Lok
production due to quality mismatch of capacity to generate 6 MW from 600 TPD Sabha that Indian cities currently have
the input garbage. waste available from Vijayawada and potential to produce around 500 MW of
These were followed by two small- Guntur set up in 2003). power through waste to energy route.
scale attempts, which were perhaps The breakup of the potential is provided
more successful. At Vijaywada, an AD Current Status in Table 1.
facility, followed by power generation, As per the Task Force Report submitted As far as the waste to energy
was installed which is designed for to Lok Sabha on waste to energy, there market is concerned, the global market
20 TPD—about 16 TPD of segregated are 2,200 waste-to-energy plants around was valued at US$25.32 billion in
municipal garbage and 4 TPD of the world. They have a disposal capacity 2013, recording a growth of 5.5% on
slaughterhouse waste. Another AD of about 255 million tonnes of waste per the previous year. Waste to energy
plant has been installed at Koyambedu year. By 2017, another 180 plants with a technologies, based on thermal
flower market with a designed capacity capacity of 52 million tonnes shall have energy conversion, led the market and
of 30 TPD. This was followed by series of
decentralized AD plants utilizing food
100
waste from hotels and restaurants in
Pune and as on date, there are around 80
20 such plants functioning in the city no. of plants [-]
in the range of 1–10 TPD capacity. The 60
biogas generated is processed into
40
power which is used for street lighting.
The work on processing waste to 20
generate Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)
and then use it for thermal or power 0
applications began in England as Austria Belgium Denmark Finland France Germany Hungary Ireland Italy Norway Portugal Spain Sweden Switzerland USA
construction began at Byker, New Castle Czech Republic The Netherlands United Kingdom
and Doncaster, South Yorkshire in 1976
(Warmer Bulletin, No. 39, 1993, Kent, UK). Figure 2: Waste to energy plants in Europe and US
July–September 2018 18 energy future
these, two are in Delhi and one is in one in Germany in 1981, Laval (France), technologies have been commercially
Jabalpur at various levels of maturity. Chatel St. Denis (Switzerland), five plants deployed, especially in Europe, Japan,
Anaerobic digestion-based MSW to in Sweden, and one 800 TPD capacity Australia, China, and the USA. In the
energy projects got commissioned by plant at Edin Prairie, Minnesota, USA. The USA, there are 86 WtE plants—about
utilizing the incentive schemes of the RDF was used for generating power or 12% of waste is combusted for energy
Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy used in cement plants. recovery—mostly ‘mass burn’. The
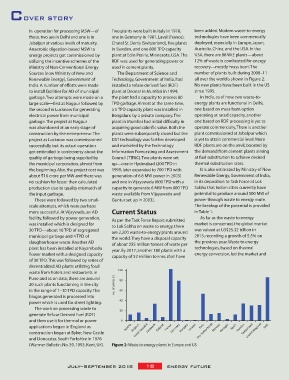
Sources (now Ministry of New and The Department of Science and number of plants built during 2008–11
Renewable Energy), Government of Technology, Government of India, had all over the worldis shown in Figure 2.
India. A number of efforts were made installed a refuse derived fuel (RDF) No new plants have been built in the US
to install facilities for AD of municipal plant at Deonar in Mumbai in 1994; since 1995.
garbage. Two attempts were made on a the plant had a capacity to process 80 In India, as of now, two waste-to-
large scale—first at Nagpur followed by TPD garbage. Almost at the same time, energy plants are functional in Delhi,
the second in Lucknow for generating a 5 TPD capacity plant was installed in one based on mass burn option
electrical power from municipal Bengaluru by a private company. The operating at rated capacity, another
garbage. The project at Nagpur plant in Mumbai had initial difficulty in one based on RDF processing is yet to
was abandoned at an early stage of acquiring good calorific value. Both the operate commercially, There is another
construction by the entrepreneur. The plants were subsequently closed but the plant commissioned at Jabalpur which
project at Lucknow was commissioned DST technology was further developed is yet to attain commercial level. More
successfully but its actual operation and marketed by the Technology RDF plants are on the anvil, boosted by
got embroiled in controversy about the Information Forecasting and Assessment the demand from cement plants aiming
quality of garbage being supplied by Council (TIFAC). Two plants were set at fuel substitution to achieve desired
the municipal corporation, almost from up—one in Hyderabad (200 TPD in thermal substitution rates.
the beginning. Also, the project cost was 1999, later expanded to 700 TPD with It is also estimated by Ministry of New
about `16 crore per MW and there was generation of 6.6 MW power in 2003) Renewable Energy, Government of India,
no cushion for lesser than calculated and one in Vijayawada (600 TPD with a in its deposition to Task Force at Lok
production due to quality mismatch of capacity to generate 6 MW from 600 TPD Sabha that Indian cities currently have
the input garbage. waste available from Vijayawada and potential to produce around 500 MW of
These were followed by two small- Guntur set up in 2003). power through waste to energy route.
scale attempts, which were perhaps The breakup of the potential is provided
more successful. At Vijaywada, an AD Current Status in Table 1.
facility, followed by power generation, As per the Task Force Report submitted As far as the waste to energy
was installed which is designed for to Lok Sabha on waste to energy, there market is concerned, the global market
20 TPD—about 16 TPD of segregated are 2,200 waste-to-energy plants around was valued at US$25.32 billion in
municipal garbage and 4 TPD of the world. They have a disposal capacity 2013, recording a growth of 5.5% on
slaughterhouse waste. Another AD of about 255 million tonnes of waste per the previous year. Waste to energy
plant has been installed at Koyambedu year. By 2017, another 180 plants with a technologies, based on thermal
flower market with a designed capacity capacity of 52 million tonnes shall have energy conversion, led the market and
of 30 TPD. This was followed by series of
decentralized AD plants utilizing food
100
waste from hotels and restaurants in
Pune and as on date, there are around 80
20 such plants functioning in the city no. of plants [-]
in the range of 1–10 TPD capacity. The 60
biogas generated is processed into
40
power which is used for street lighting.
The work on processing waste to 20
generate Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)
and then use it for thermal or power 0
applications began in England as Austria Belgium Denmark Finland France Germany Hungary Ireland Italy Norway Portugal Spain Sweden Switzerland USA
construction began at Byker, New Castle Czech Republic The Netherlands United Kingdom
and Doncaster, South Yorkshire in 1976
(Warmer Bulletin, No. 39, 1993, Kent, UK). Figure 2: Waste to energy plants in Europe and US
July–September 2018 18 energy future